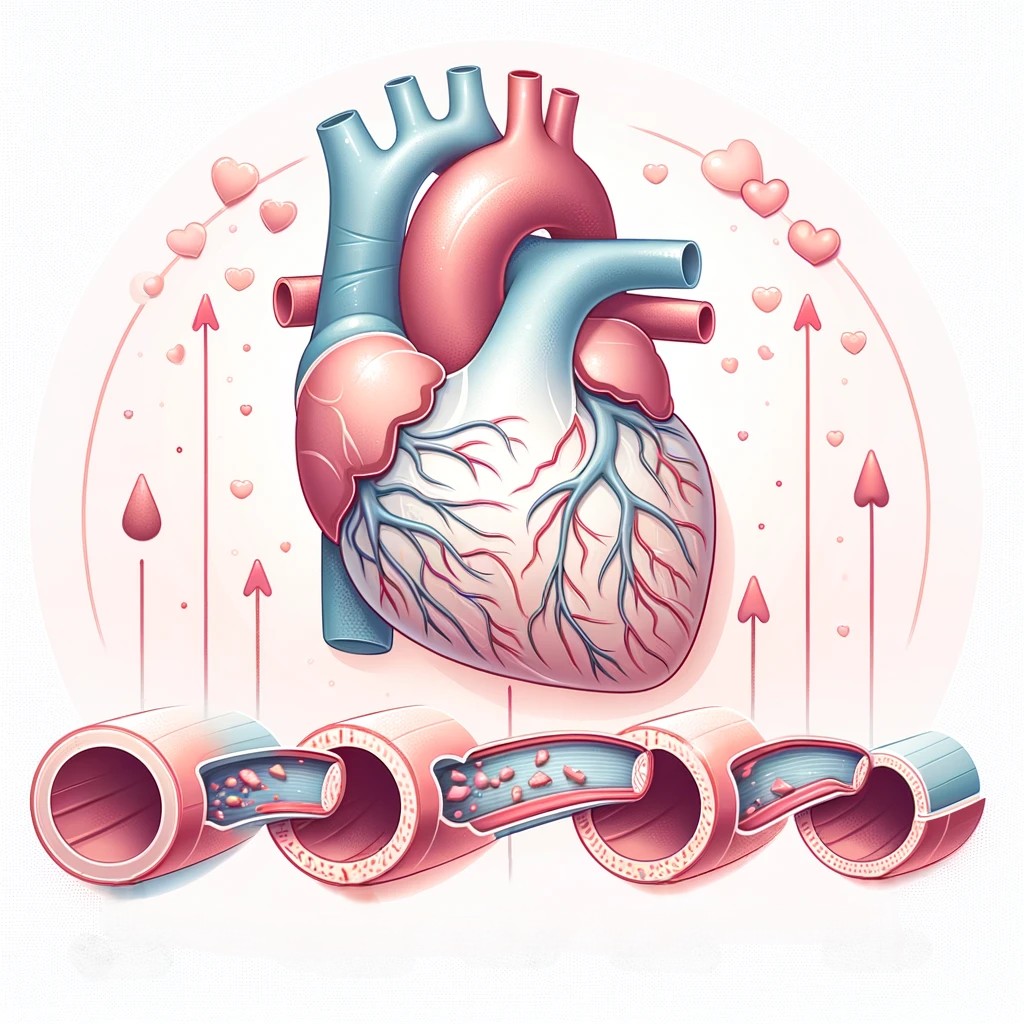
2. What Are The Symptoms Of Coronary Artery Disease?
The most prevalent symptom of coronary artery disease is chest discomfort, which is also known as
angina.
Symptoms of coronary artery disease may vary between men and women. As an example, men are
more likely to experience chest pain. In addition to chest tightness, women are more prone to have
shortness of breath, nausea, and excessive exhaustion.
Common symptoms are:
Tightness, pain, and pressure in the chest.
Breathing difficulty
Heart attack
Pain in the upper abdomen; the neck; the jaw; or the back
Pain, numbness, weakness, and coldness can occur in the legs and arms if the blood vessels in those
areas become narrowed.
3.What Are The Causes Of Coronary Artery Disease?
Cholesterol deposits (plaques) in the coronary arteries are typically the leading cause of coronary
artery disease. The accumulation of these plaques is known as atherosclerosis or arterial stiffening.
Plaque is an accumulation of fatty streaks that causes the artery walls to become thick and rigid. It
decreases blood flow to the heart and other organs. It could cause a heart attack, chest pain, or a
stroke.
During time, plaque might harden or burst (break open). Plaque that has hardened narrows
coronary arteries and decreases the flow of oxygen rich blood to the heart. On the plaque’s surface, a
blood clot can form if it ruptures. A big blood clot can obstruct coronary artery blood flow to a
significant or total degree. Over time, burst plaque also causes coronary arteries to stiffen and
narrow.
4. Diagnosis Of Coronary Heart Disease?
Your doctor will diagnose coronary heart disease (CAD) based on your medical and family histories, your
risk factors for CAD, the results of tests and procedures, and a physical examination. There is
currently no reliable single test for determining CAD.
It is possible for coronary artery disease to be undetected until a heart attack, stroke, or heart
failure occurs. It is essential to monitor cardiac symptoms and consult a physician if you have grave
concerns. Routine health checkups may detect heart (cardiovascular) disease in its earliest
stages.
To find out about your condition, the doctor will suggest some test like: –
Electrocardiogram
Echocardiogram
CT Scan of heart
Cardiac catheterization
Exercise stress test
Nuclear stress test
Blood tests (To check levels of certain fats, cholesterol, sugar, and proteins in your blood)
Coronary Angiography and Cardiac Catheterization‐ This test uses dye and special x rays to show the
insides of your coronary arteries.
5. What Are The Risk Factors Of Coronary Artery Disease?
Heart disease risk factors are conditions or habits that make you more likely to develop heart disease.
Some risk factors for coronary heart disease are modifiable and, others are not.
High levels of cholesterol and blood pressure
Age and sex of the person
Diabetes
Family history (if any member of the family had heart disease)
Taking a lot of stress and sleeping less
Eating an unhealthy diet
Drinking alcohol or smoking
Lack of physical activity
Any of the risk factors can be the reason of your coronary heart disease.
6.How Is Coronary Artery Disease Dealt With?
The standard treatment for coronary artery disease includes lifestyle modifications such as stopping
smoking, eating healthily, and exercising more. Sometimes, medications and procedures are
required.
Recommended Medications:
Cholesterol medications: Medications can reduce LDL cholesterol and reduce plaque formation in the
arteries.
Aspirin: Aspirin prevents blood clots and aids in their treatment. As a primary preventative measure
against a heart attack or stroke, daily low-dose aspirin may be recommended for certain individuals.
Regular aspirin use may induce major side effects, such as gastrointestinal and intestinal hemorrhage.
Don’t take aspirin daily without consulting your doctor.
Beta-blockers: These medications reduce heart rate. In addition, they lower blood pressure. If you have
already suffered a heart attack, beta blockers may reduce your risk of a second one.
Calcium channel blockers: If you cannot use beta blockers or if they do not work for you, one of these
drugs may be prescribed. Medication that blocks calcium channels can help alleviate the symptoms of
chest pain.
Angiotensin II receptor blockers and angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors (ARBs). These
medications lower blood pressure. These may prevent coronary artery disease from progressing.
Nitroglycerin – This drug widens the coronary arteries. It can alleviate or minimize chest pain.
Nitroglycerin is available in pill, spray, and patch form.
Ranolazine – Individuals experiencing chest discomfort may benefit from this medication (angina). It
can be taken alongside or in place of beta-blockers.
Do not take any medications without first seeing your doctor; it is always preferable to seek
professional assistance to improve your health.
7. Surgical Procedure To Dealt With Coronary Artery Disease?
Depending on the patient’s condition doctor may suggest any of the procedure given below:
Angioplasty
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting
Cardiac Rehabilitation
Don’t forget to take your medicine, do not wait until you need to take medication or have an upcoming
doctor’s appointment to start doing so.
Don’t miss out on any of your doctor’s visits, regular checkups with your doctor can reveal any hidden
heart problems or other health issues. Also, this can aid in diagnosing and fixing issues before they
worsen.
8. How Can Someone With Coronary Artery Disease Maintain Their Health?
Medications for common conditions such as hypertension, arrhythmia, and cholesterol.
Any surgical treatments that may assist in restoring blood flow to the heart.
Modify your lifestyle by adopting a nutritious diet, engaging in regular exercise, and giving up tobacco
and alcohol.
Follow your doctor’s rigorous dietary instructions for heart health.
Regularly adhere to your treatment plan for monitoring CAD, including checking your Blood Pressure
levels, taking your meds on time, and attending your regularly scheduled checkups for an update on your
CAD condition.
9. Coronary Artery Disease And How It Affects Your Mental Health?
A CAD diagnosis may prompt you to consider your heart and arteries in greater detail than ever before.
This can be intimidating and exhausting. You may worry a great deal about your symptoms or what may
occur. Many individuals with coronary artery disease develop depression and anxiety, which is not
surprising. You are suffering from a potentially fatal condition. Even if you have heart disease, you
can still thrive and lead a joyful, active life. See a counsellor if your diagnosis is hurting your
mental health.